HW10 詳解
問題1
page 683, chapter 10.1 Exercise 2
What kind of graph (from Table 1) can be used to model a highway system between major cities where
- there is an edge between the vertices representing cities if there is an interstate highway between them?
- there is an edge between the vertices representing cities for each interstate highway between them?
- there is an edge between the vertices representing cities for each interstate highway between them, and there is a loop at the vertex representing a city if there is an interstate highway that circles this city?
問題1
page 683, chapter 10.1 Exercise 2

What kind of graph (from Table 1) can be used to model a highway system between major cities where
- there is an edge between the vertices representing cities if there is an interstate highway between them?
- there is an edge between the vertices representing cities for each interstate highway between them?
- there is an edge between the vertices representing cities for each interstate highway between them, and there is a loop at the vertex representing a city if there is an interstate highway that circles this city?
- A simple graph would be the model here, since there are no parallel edges or loops, and the edges are undirected.
- A multigraph would in theory, be needed here. since there may be more than one interstate highway between the same pair of cities.
- A pseudograph is needed here, to allow for loops.
問題2
page 699, chapter 10.2 Exercise 8
In Exercises 7–9 determine the number of vertices and edges and
find the in-degree and out-degree of each vertex for the given
directed multigraph.

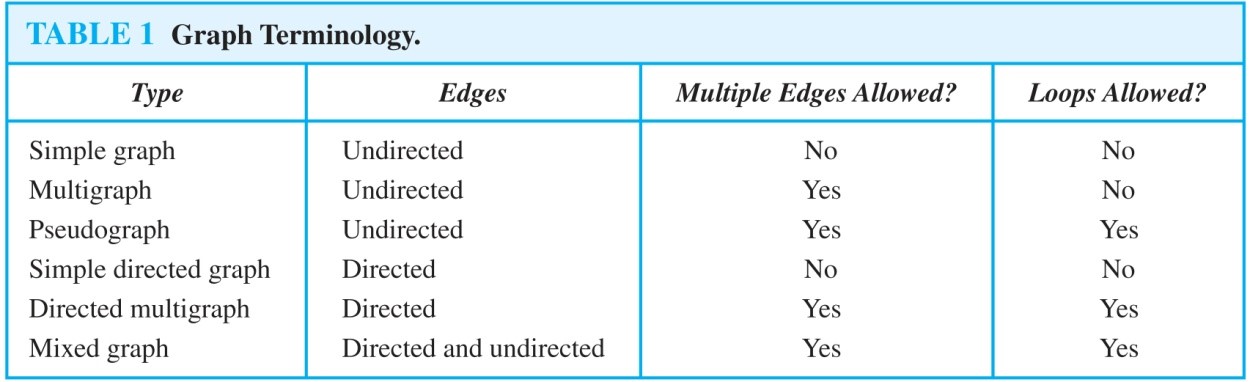
問題2
page 699, chapter 10.2 Exercise 8
In Exercises 7–9 determine the number of vertices and edges and
find the in-degree and out-degree of each vertex for the given
directed multigraph.


- deg \(^{-}(點編號) = 箭頭進入這點有幾條edge\)
- deg \(^{+}(點編號) = 箭頭出去這點有幾條edge\)
- 注意b點及d點,自己連到自己出去及近來次數要各加1
- In this directed multigraph there are 4 vertices and 8 edges.
- The degrees are deg \(^{-}(a) = 2\), deg \(^{+}(a) = 2\)
- , deg \(^{-}(b) = 3\), deg \(^{+}(b) = 4\)
- , deg \(^{-}(c) = 2\), deg \(^{+}(c) = 1\)
- , deg \(^{-}(d) = 1\), and deg \(^{+}(d) = 1\).
問題3
page 710, chapter 10.3 Exercise 8
Represent the graph in Exercise 4 with an adjacency matrix.

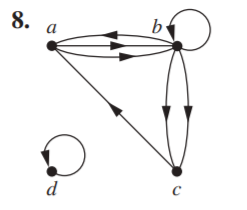
問題3
page 710, chapter 10.3 Exercise 8
Represent the graph in Exercise 4 with an adjacency
matrix.


adjacency matrix(鄰接矩陣):
把一張圖上的點依序標示編號(abc),然後我們建立一個方陣來記錄其連接資訊,方陣中的每一個element都代表著某兩點的連接資訊。
e.g. a->b, 會在(a,b)處紀錄1

This is similar to Exercise 7. \(\begin{bmatrix} 0 & 1 & 0 & 1 & 0
\\ 1 & 0 & 1 & 1 & 1 \\ 0 & 1 & 1 & 0 & 0 \\ 1 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 \\
0 & 0 & 1 & 0 & 1 \\ \end{bmatrix}\)
問題4
page 724, chapter 10.4 Exercise 2
Does each of these lists of vertices form a path in the
following graph? Which paths are simple? Which are circuits?
What are the lengths of those that are paths?
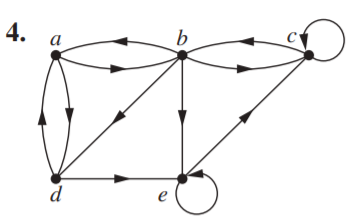
- a, b, e, c, b
- a, d, a, d, a
- a, d, b, e, a
- a, b, e, c, b, d, a

問題4
page 724, chapter 10.4 Exercise 2
Does each of these lists of vertices form a path in the
following graph? Which paths are simple? Which are circuits?
What are the lengths of those that are paths?

- a, b, e, c, b
- a, d, a, d, a
- a, d, b, e, a
- a, b, e, c, b, d, a

- path: 指的是從起點開始到終點結束來拜訪一個graph
- a circuit: 的起始與結束都是在同一個頂點
- length: 圖的edge數量
- A path or circuit is simple: 該圖沒有包含大於一次相同edge
- This is a path of length 4, but it is not a circuit, since it ends at a vertex other than the one at which it began. It is simple,since no edges are repeated.
- This is a path of length 4, which is a circuit. It is not simple, since it uses an edge more than once.
- This is not a path,since there is no edge from d to b.
- This is not a path,since there is no edge from b to d.
問題5
page 741, chapter 10.5 Exercise 54
A diagnostic message can be sent out over a computer network to
perform tests over all links and in all devices. What sort of
paths should be used to test all links? To test all devices?
問題5
page 741, chapter 10.5 Exercise 54
A diagnostic message can be sent out over a computer network to
perform tests over all links and in all devices. What sort of
paths should be used to test all links? To test all devices?
-
An Euler path is a path that uses every
edge of a graph exactly once.
An Euler path starts and ends at different vertices. -
An Euler circuit is a circuit that uses every edge of a graph exactly once.
An Euler circuit starts and ends at the same vertex.
- Hamiltonian Path – A simple path in a graph G that passes through every vertex exactly once is called a Hamiltonian path.
- Hamiltonian Circuit – A simple circuit in a graph G that passes through every vertex exactly once is called a Hamiltonian circuit.
An Euler path will cover every link, so
it can be used to test the
links. A Hamilton path will cover all the devices, so it can
be
used to test the devices.
問題6
page 753, chapter 10.6 Exercise 26
Solve the traveling salesperson problem for this graph by
finding the total weight of all Hamilton circuits and
determining a circuit with minimum total weight.
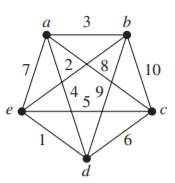

問題6
page 753, chapter 10.6 Exercise 26
Solve the traveling salesperson problem for this graph by
finding the total weight of all Hamilton circuits and
determining a circuit with minimum total weight.


- 著名的旅行推銷員問題 (TSP)要求其應採取的最短路線來訪問一組城市。
- 這個問題總結為找到一個Hamilton circuit,使得其路徑的權重總和盡可能最小。
- 這個問題也是NP-complete,因此利用暴力法不可行,可能要運用像是動態規劃法、類似Dijkstra的最小路徑貪婪法等
e. 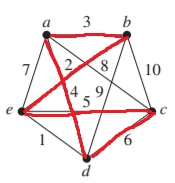 f.
f. 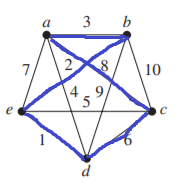
 f.
f. 
The following table shows twelve different Hamilton circuits and
their weights:
The circuits a-b-e-c-d-a and a-b-e-d-c-a are the ones with minimum total weight.
- Circuit: a-b-c-d-e-a, Weight = \(3 + 10 + 6 + 1 + 7 = 27\)
- Circuit: a-b-c-e-d-a, Weight = \(3 + 10 + 5 + 1 + 4 = 23\)
- Circuit: a-b-d-c-e-a, Weight = \(3 + 9 + 6 + 5 + 7 = 30 \)
- Circuit: a-b-d-e-c-a, Weight = \(3 + 9 + 1 + 5 + 8 = 26 \)
- Circuit: a-b-e-c-d-a, Weight = \(3 + 2 + 5 + 6 + 4 = 20\)
- Circuit: a-b-e-d-c-a, Weight = \(3 + 2 + 1 + 6 + 8 = 20\)
- Circuit: a-c-b-d-e-a, Weight = \(8 + 10 + 9 + 1 + 7 = 35\)
- Circuit: a-c-b-e-d-a, Weight = \(8 + 10 + 2 + 1 + 4 = 25 \)
- Circuit: a-c-d-b-e-a, Weight = \(8 + 6 + 9 + 2 + 7 = 32\)
- Circuit: a-c-e-b-d-a, Weight = \(8 + 5 + 2 + 9 + 4 = 28\)
- Circuit: a-d-b-c-e-a, Weight = \(4 + 9 + 10 + 5 + 7 = 35\)
- Circuit: a-d-c-b-e-a, Weight = \(4 + 6 + 10 + 2 + 7 = 29\)
The circuits a-b-e-c-d-a and a-b-e-d-c-a are the ones with minimum total weight.
問題7
page 761, chapter 10.7 Exercise 14
Suppose that a connected planar graph has 30 edges. If a planar
representation of this graph divides the plane into 20 regions,
how many vertices does this graph have?
問題7
page 761, chapter 10.7 Exercise 14
Suppose that a connected planar graph has 30 edges. If a planar
representation of this graph divides the plane into 20 regions,
how many vertices does this graph have?
Euler Formula
For any convex polyhedron, the number of vertices and faces together is exactly two more than the number of edges.
$ v(頂點) - e(邊) + r(面) = 2$
Euler's formula says that \(v - e + r = 2\) We are given \(e = 30
\) and \(r = 20\). Therefore \(v = 2 - r + e = 2-20+30 = 12\).
問題8
page 768, chapter 10.8 Exercise 6
In Exercises 5–11 find the chromatic number of the given
graph.
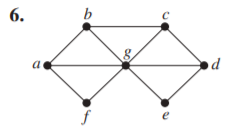

問題8
page 768, chapter 10.8 Exercise 6
In Exercises 5–11 find the chromatic number of the given
graph.


- 點著色問題(Vertex Coloring): np-complete,指的是每個點塗上不同的顏色,鄰點不可相同顏色。
- 最小點著色(Chromatic Number): 指的是以最少的顏色來完成點著色問題。
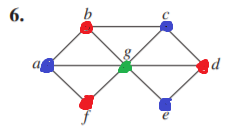
Since there is a triangle, at least 3 colors are needed. To show
that 3 colors suffice,notice that we can color the vertices around
the outside alternately using red and blue, and color vertex \(g\)
green.
Reference
參考文獻
- http://web.ntnu.edu.tw/~algo/Graph.html
- https://math.stackexchange.com/questions/456999/are-my-answers-correct-graphs-paths-path-lengths-circuits
- https://jlmartin.ku.edu/courses/math105-F11/Lectures/chapter5-part2.pdf
- http://bonjuniors.blogspot.com/2012/09/blog-post_4.html
- https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/mathematics-euler-hamiltonian-paths/
- http://www.math.ncu.edu.tw/~chern/teach/11.pdf
- http://web.ntnu.edu.tw/~algo/Coloring.html
- https://ithelp.ithome.com.tw/articles/10279620